-
[백준 1525] 퍼즐알고리즘/BFS 2019. 12. 31. 20:21
Type : BFS
접근
문자열 BFS 트리 탐색을 통해 주어진 상태로 부터 목표 상태까지 도달 할 수 있는 최소 거리를 구한다.
Tree Example 123495786 193425786 913425789 139425789(1) 위치 및 현재 상태 파악
string cs = q.front(); int cp = cs.find('0'); int sy = cp / 3; int sx = cp % 3;2차원 배열을 사용하지 않고 몫과 나머지를 통해 y와 x 값을 도출 할 수 있다
(2) 만족한 범위 내에서 요소의 순서를 바꾼 새로운 문자열(상태)을 생성 한다.
int ny = sy + dy[i]; int nx = sx + dx[i]; np = ny*3 + nx; swap(ns[cp], ns[np]);(3) 만약 한번 이상 방문한 문자열 이면 건너 띈다/
if(dist.count(ns)>0) continue;상태 방문 순서를 기록하기 위해 map<string, int> 자료 구조를 사용한다
(4) 만약 현재 문자열이 정리된 문자열 이라면 도달 거리를 반환 한다.
if(cs == ANS) return dist[cs];플로우 차트
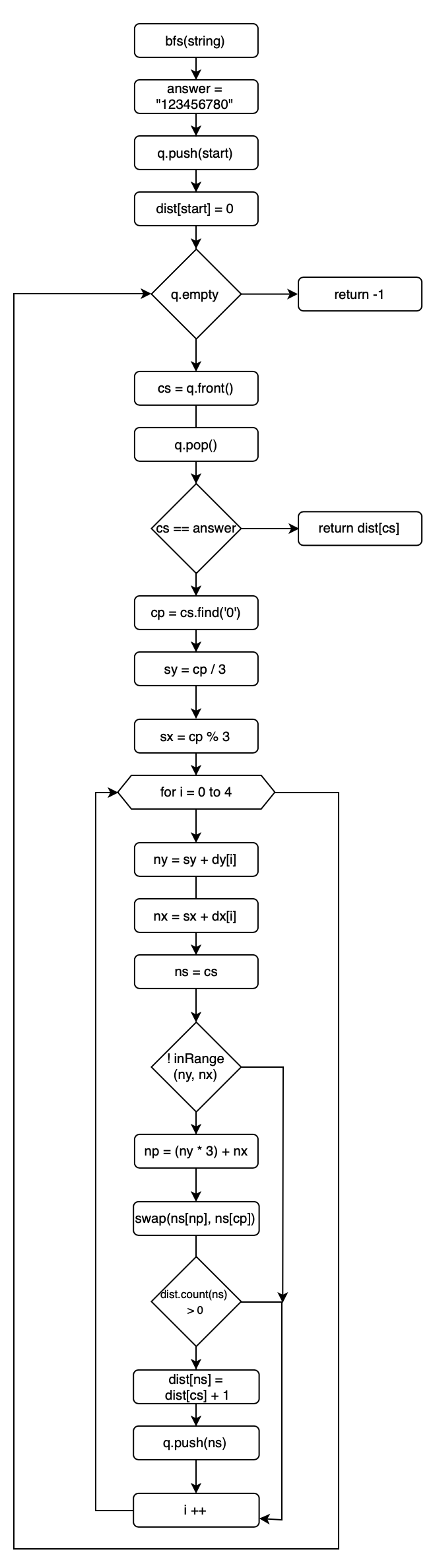
구현 코드
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <map> #include <queue> #include <string> #define ANS "123456780" using namespace std; int dy[4] {-1, 1, 0, 0}; int dx[4] {0, 0, -1, 1}; map<string, int> dist; bool inRange(int y, int x){ return 0<=y && y < 3 && 0<=x && x<3; } int bfs(string start){ string cs, ns; int sy, sx, ny, nx; int cp, np; queue<string> q; dist[start] = 0; q.push(start); while(!q.empty()){ cs = q.front(); q.pop(); if(cs == ANS) return dist[cs]; cp = (int)cs.find('0'); sy = cp/3; sx = cp%3; for(int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++){ ny = sy + dy[i]; nx = sx + dx[i]; ns = cs; if(!inRange(ny, nx)) continue; np = ny*3 + nx; swap(ns[cp], ns[np]); if(dist.count(ns)>0) continue; dist[ns] = dist[cs] +1; q.push(ns); } } return -1; } void build(string& start){ char ch; for(int y = 0 ; y < 3; y++){ for(int x = 0 ; x < 3 ; x++){ cin>>ch; start += ch; } } } int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { string start; build(start); cout<<bfs(start)<<endl; return 0; }깨달은 점
- 문자열 상태 탐색을 통해 BFS를 실시 할 수 있다
- 상태 방문을 위해 map 자료구조를 활용 할 수 있다.
- 2차원 배열 대신 몫과 나머지를 활용할 수 있다.
'알고리즘 > BFS' 카테고리의 다른 글
[백준 9328] 열쇠 (0) 2020.01.01 [백준 2251] 물통 (0) 2019.12.31 [백준 13913] 숨바꼭질 4 (0) 2019.12.31 [백준 15558] 점프게임 (0) 2019.12.13 [백준 6087] 레이저통신 (0) 2019.12.09